The Fore Brain and its Functions
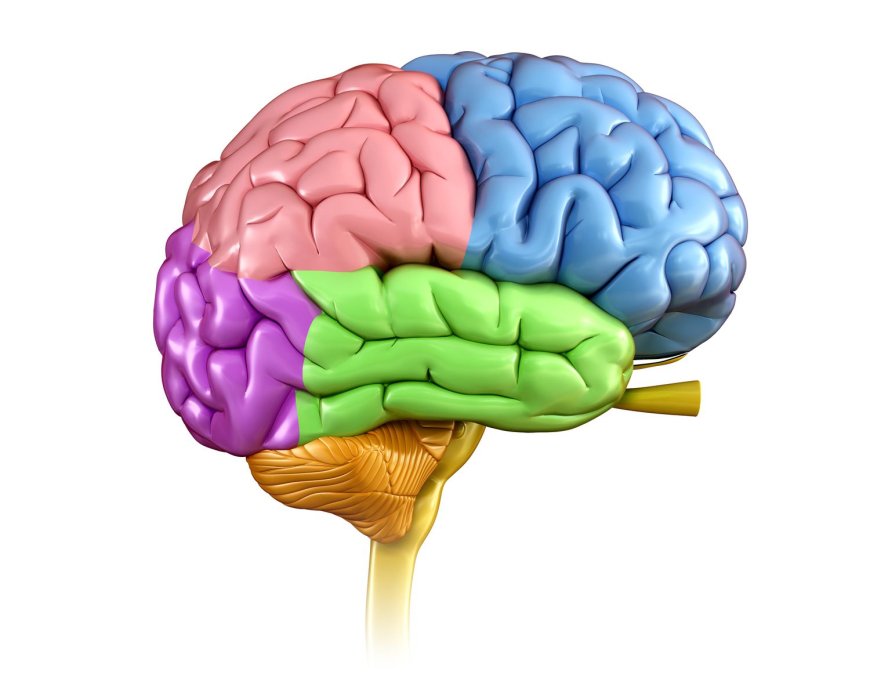
The brain is a complex organ that manages every bodily function, including thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, respiration, temperature, and hunger. The central nervous system, sometimes known as the (CNS) is made up of the spinal cord that emerges from the brain.
In a typical adult, the brain weighs roughly 3 pounds and contains 60% fat. Salts, water, protein, and carbohydrates make up the remaining 40% of the body. The brain is not made up of muscles, it is a composite of neurons, blood arteries, glial cells, and nerves.
The human brain can be divided into three basic units; Forebrain, Midbrain, and Hindbrain. This article will concentrate only on the forebrain, its parts, and its functions.
THE FOREBRAIN
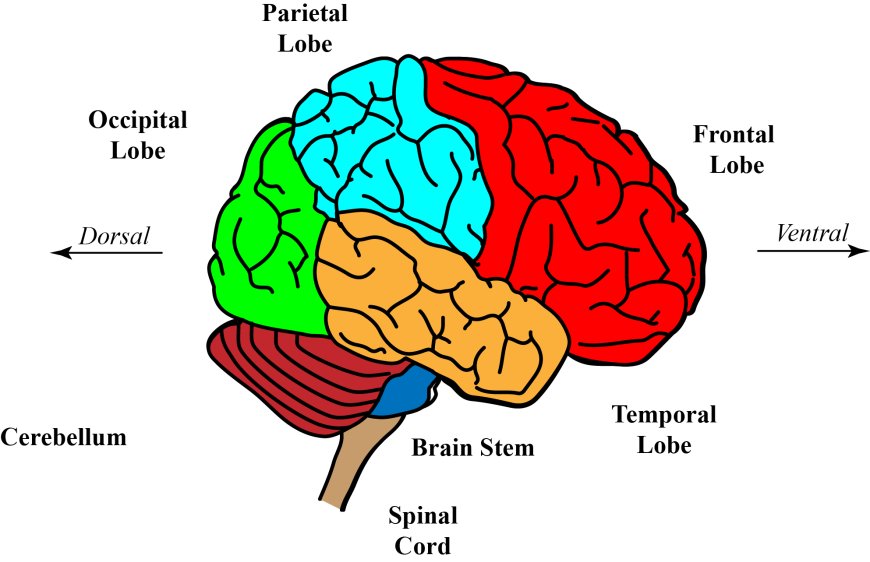
The forebrain also known as the prosencephalon is the uppermost and anterior part of the brain. It controls the reproduction system, body temperature, emotions, hunger, and sleep. The forebrain consists of the Cerebrum, Thalamus, and hypothalamus.
- Cerebrum- This is the largest part of the brain. It is the uppermost region of the Central Nervous System. The cerebrum houses the Cerebral Cortex and it is composed of two cerebral hemispheres each consisting of four (4) lobes namely: Temporal lobe, Parietal lobe, Occipital lobe, and Frontal lobe.
FUNCTIONS OF THE CEREBRUM
The cerebrum is responsible for;
- Thinking
- Intelligence
- Consciousness
- Memory
- Interpretation of touch
- Problem-solving and
- Learning
- Thalamus- The thalamus is the gateway to the mind. It is the structure at the center of the cerebral hemisphere which is a relay station for sensory pathways and for brain stem. It is also a relay station for the cerebellar and the subcortical pathways to the cortex, as well as the relay station between different cortical areas.
The thalamus is known as the relay station of all incoming motor (movement) and sensory information i.e. hearing, taste, sight, and touch.
NOTE: The only sensory information that is not relayed by the thalamus to the cerebral cortex is information related to smell (olfactory).
FUNCTIONS OF THE THALAMUS
The thalamus is responsible for;
- Relay station
- Attention
- Consciousness
- Sleep
- Hypothalamus- The ventral brain area called the hypothalamus is where the endocrine system is regulated. It receives numerous signals from various parts of the brain, and in response, it releases both releasing and inhibiting hormones.
These hormones then act on the pituitary gland to control the activities of the thyroid, adrenal, and reproductive organs, as well as growth, fluid balance, and milk production.
Along with regulating the autonomic nervous system, regulating body temperature, and regulating appetite, it also plays an integral part in non-endocrine processes.
FUNCTIONS OF HYPOTHALAMUS
The hypothalamus is responsible for;
- The body homeostasis
- Regulation of body temperature
- Regulation of appetite
- Breast milk production
- Growth
- Sex drive
- Sleep-wake cycles
- Thirst and
- Weight control
What's Your Reaction?





























































































